
How to reproduce it (as minimally and precisely as possible): Kubectl port-forward is getting connection refused from nifi service port 80 Perhaps running kubectl port-forward in the background would be better (see: Perform kubectl port-forward in background).Cannot get access to ui when deployed to microk8s. NOTE: I just want you to pay attention to the -network=host option (I used the same container as before): docker run -it -name=k8s-conn-12 -network=host -v /config:/config mattjcontainerregistry/forward:latest kubectl port-forward service/postgres 2223:5432 -kubeconfig=configĪgain, we can check if it works as expected from outside the container: psql -U postgres -h localhost -p 2223Īdditionally, it's worth considering if you really need a docker container for port forwarding. Host: For standalone containers, remove network isolation between the container and the Docker host, and use the host’s networking directly. This approach requires the use of a host network: WARNING: psql major version 11, server major version 13. In addition, we can do the same from the host machine (from outside the container with the exposed and published port): psql -U postgres -h localhost -p 2223 WARNING: psql major version 12, server major version 13. docker run -it -name=k8s-conn-12 -p 2223:2223 -v /config:/config mattjcontainerregistry/forward:latest kubectl port-forward -address $(hostname -i),localhost service/postgres 2223:5432 -kubeconfig=configįrom another terminal tab we can check if it works: docker exec -it k8s-conn-12 psql -U postgres -h localhost -p 2223 I just want you to pay attention to the kubectl port-forward -address $(hostname -i),localhost service/postgres 2223:5432 command. NOTE: I used a container with kubectl already installed. This approach is very similar to yours, I just added the -address argument: NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE I will briefly describe both solutions to show you how it works.įirst, I prepared postgres: # kubectl get pod,svc If you use the host network mode for a container, that container’s network stack is not isolated from the Docker host (the container shares the host’s networking namespace), and the container does not get its own IP-address allocated. As may be found in the Docker host networking documentation: To solve your problem, you can use the host network instead of the bridge network.

All newly-started containers connect to a default bridge network unless otherwise specified.By default, kubectl binds only to localhost and therefore it does not work as you expect (see: Kubectl Reference Docs). You can add the -address argument to the kubectl port-forward command with the IP address of the container running this command.I think there are two possible solutions that may help in your case: What I am not able to do is to connect from outside the container with the exposed and published port
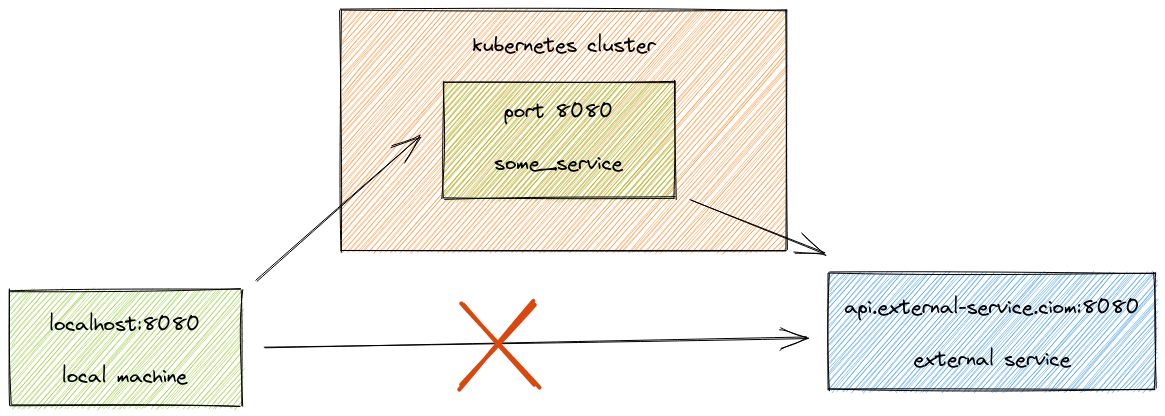
So the port forwarding is successful, and I am able to connect to the postgres instance from inside the docker container. Output of the docker run command: Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:2223 -> 5432 However, when I do docker exec -ti to the said container and run the above psql command, I am able to connect to postgres.ĬMD ĭocker Run command: docker run -it -name=k8s-conn-12 -p 2223:2223 my_image_name:latest This probably means the server terminated abnormally Now when I am trying to access the postgres through psql -h localhost -p 2223, I am getting the following error: psql: server closed the connection unexpectedly Then I ran the container by publishing the said port ( -p 2223:2223)

In the Dockerfile, I have exposed the relevant port 2223. I have a docker container which is running kubectl port-forward, forwarding the port (5432) of a postgres service running as a k8s service to a local port (2223).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
